Review the Best Practices Guidelines
The Best Practices for Sustainability and Sustainability-Related degrees and certificates consist of standards in four core areas focusing on academic programs, and four support areas integral to exemplary Sustainability Education at institutions of higher education.
The Best Practices were identified from stakeholder input from over 300 faculty, administrators, students, recent alumni, and employers. The Global Council for Science and the Environment’s Sustainability Education Community of Practice workshopped these standards in twice-monthly virtual meetings from 2023-2024.
Below is an Overview and Roadmap of the synthesized Best Practices. Candidates for accreditation receive a workbook: Guidelines towards Accreditation document which contains the definitions, evidence, expectations, and exemplars for how programs can meet or exceed these standards to lead their institutions in Sustainability Education.
Specializations / Sustainability Topics
The 4+4=8 Best Practices also feature a unique opportunity for programs to identify a self-selected area of Specialization as a Sustainability Topic to weave through their self-assessment. This topic can reflect institutional priorities, faculty expertise, and/or regional emphasis. While of course a program may have more than one area of specialization, defining and sharing a focused topic is beneficial for prospective students, and to develop networks of programs working in focused areas of Sustainability (Examples include: Food, Energy, Water, Leadership, Economy, Education).
Specializations / Transformative Themes
Programs are also encouraged to self-select a Transformative Theme that represents the leading edge of their program – a value that characterizes the aspirations of the program. This self-selected transformative theme is woven throughout the 4+4=8 Best Practice areas to guide continued evolution and improvement of the program. The Transformative Theme may be shared publicly or kept private as an institutional goal.
Roadmap of the 4 Core Areas:
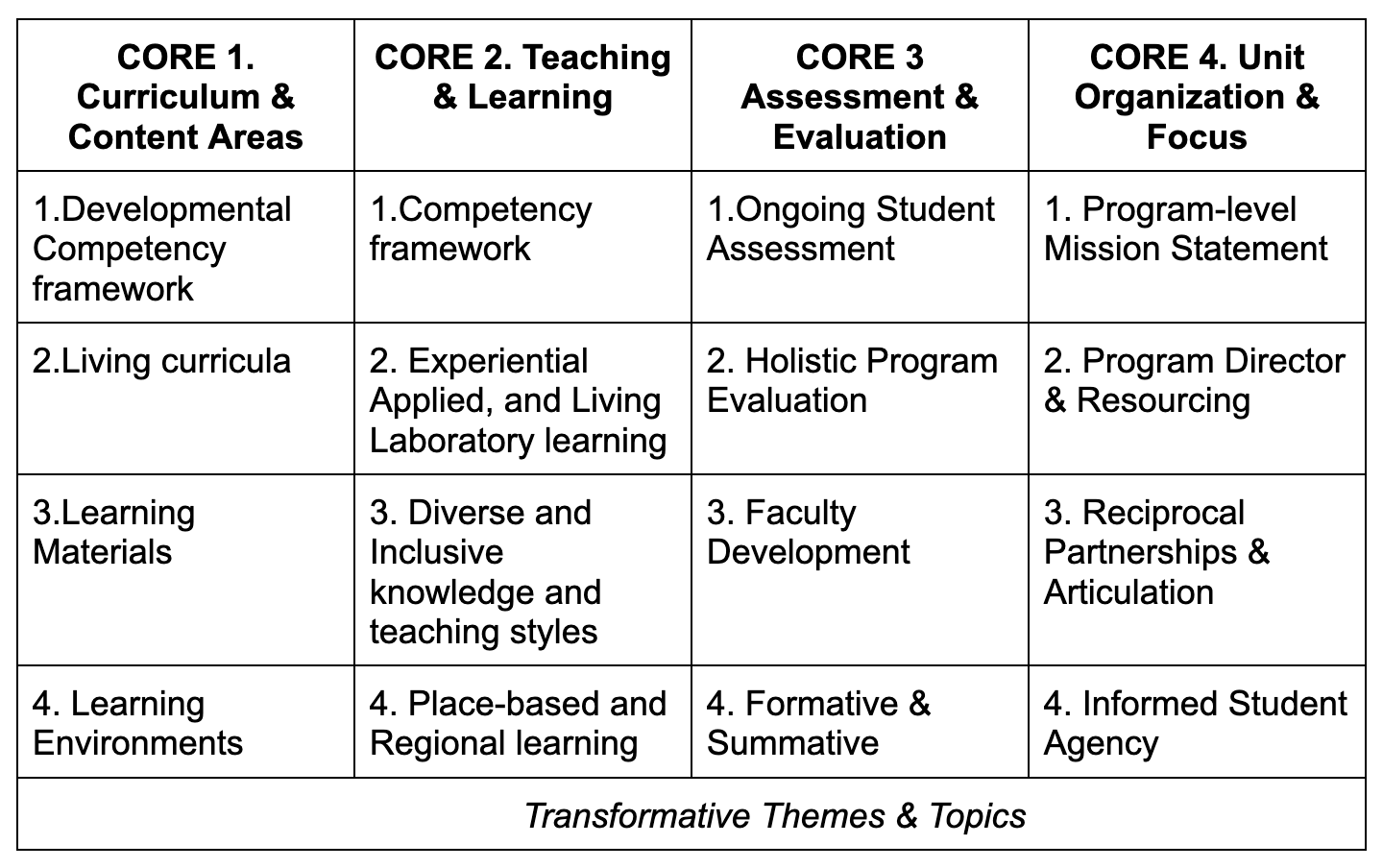
There are four core areas of 1) Curriculum & Content, 2) Teaching & Learning 3), Assessment and Evaluation and (4) Unit Organization & Focus. Table 1 provides an overview of best practices in these core areas.
Table 1: CORE
Roadmap of the 4 Support Areas:
These are the four essential support areas of Leadership & Mission, Campus & Community, Student Support, and Faculty Support. Table 2 provides an overview of best practices in these areas.
Table 2: SUPPORT
Definitions
This section adds the basic definition of each core and support area, as well as a basic description of each standard in that area. Additional guidance, including Evidence, Expectations, and Examples, will be developed through workshop engagement in Fall 2024 as we continue to iterate with program directors.
Core Area 1: Curriculum & Content
This area describes topics and progression of material presented to students in courses and class experiences.
CORE 1, Standard 1: Developmental Competency Framework
C1.S1 A competency framework* guides the creation of program learning outcomes that students develop across multiple courses.
CORE 1, Standard 2: Living Curricula
C1.S2 Program curricula is responsive to the needs of students, employers, and communities.
CORE 1 Standard 3: Learning Materials
C1.S3 Program incorporates diverse learning materials (i.e, readings, speakers, and/or activities), and draws from inter- and trans- disciplinary perspectives as well as multiple ways of knowing.
CORE 1 Standard 4: Learning Environments
C1.S4 Program incorporates diverse learning environments including outdoor and field -based experiences that reflect and develop sense of place.
Core Area 2: Teaching & Learning
This area describes pedagogical approaches, teaching strategies and student learning experiences.
CORE 2, Standard 1: Engagement with Key Competencies
C2.S1 Student learning experiences provide them with opportunities to self-reflect and cultivate capacities related to the key competencies in sustainability
CORE 2, Standard 2: Experiential, Applied, and Living Laboratory Learning
C2.S2 Students participate in experiential and applied learning activities and capstone experiences that engage them with sustainability challenges, perspectives, and solutions.
CORE 2, Standard 3: Diverse and inclusive knowledge
C2.S3 Teaching styles include and foster multiple perspectives, cultures, and voices
CORE 2, Standard 4: Place Based and Regional Learning
C2.S4 Curricula and experiences are contextualized locally.
Core Area 3: Assessment & Evaluation
Both formative and summative methods are used in a spirit of continuous improvement including multiple methods of regular Assessment (how student learning is assessed, communicated, and utilized), and Evaluation, which refers to program evaluation for improvement, including areas of evaluation and methods used.
CORE 3, Standard 1: Ongoing Assessment
C3.S1 The program has a plan for ongoing assessment of diverse learning domains and increasing student proficiency and real-world achievement of program competencies/outcomes.
CORE 3, Standard 2: Holistic Evaluation
C3.S2 Programs use holistic approaches to evaluate different dimensions of program success and leverage information and feedback for continuous program improvement.
CORE 3, Standard 3: Faculty Development and Evaluation
C3.S3 Ongoing professional development for sustainability is provided; criteria for faculty evaluation and promotion include sustainability education
CORE 3 Standard 4: Formative and Summative
C3.S4 Clear Expectations and processes for student assessment and program evaluation include Include both formative and summative guidance.
Core Area 4: Unit Organization & Focus
Standards in this area describe a program-level structure and commitment to sustainability. A specific unit has been formed to provide multi, inter, and transdisciplinary education.
CORE 4, Standard 1: Program-level Mission Statement
C4.S1 The program has a program-level mission statement* that is consistent with the purpose and values of sustainability education as well as the institution, region, and local cultural influences.
*Sustainability and Sustainability-Related degree pathways should be evaluated together as an ecosystem. Institutions with certificate, associate’s, baccalaureate, master’s, or Ph.D. programs should have a separate mission statement for each degree.
CORE 4, Standard 2: Program Director & Resourcing
C4.S2 A qualified program director or team is appointed with adequate fiscal and other resources.
CORE 4, Standard 3: Reciprocal partnerships
C4.S3 Programs actively foster continuous, coordinated, resourced and reciprocal relationships with community partners.
CORE 4, Standard 4: Informed Student Agency
C4.S4 The program provides pathways, emphases, or certificates that allow students to customize their degree.
Support Area 1: Leadership and Mission
This area describes the commitment and participation of senior level administrators (provost, president) and the institutional commitment to sustainability in overall institutional planning and action.
SUPPORT 1, Standard 1: Sustainability Commitment
S1.S1 The institution has a clear commitment to sustainability.
SUPPORT 1, Standard 2: Sustainability as Key Performance Objective
S1.S2. The institution recognizes sustainability as a key performance objective.
SUPPORT 1, Standard 3: Institutional Culture
S1.S3. Leadership facilitates a supportive institutional culture and sense of belonging.
SUPPORT 1, Standard 4: Local and Global Impact
S1.S4. Institutional and program-level leadership acts to enable local and global impact in sustainability.
Support Area 2: Campus & Community
This area describes visible commitment to local community relationships and to sustainability across and beyond campus.
SUPPORT 2, Standard 1: Campus Built Environment
S2.S1 Campus built environment, planning and operations support sustainability education curricula.
SUPPORT 2, Standard 2. Campus Ecological Environment
S2.S2 The campus ecological/biological environment reflects and supports a commitment to preserving, protecting, and regenerating the biological/ecological environment.
SUPPORT 2 Standard 3: Campus Cultural Environment
S2.S3: The campus cultural environment reflects and supports a future-thinking culture of sustainability, participation, inclusion and belonging.
SUPPORT 2, Standard 4: Impact Assessment
S2.S4 Long-term campus and community impacts are assessed.
Support Area 3: Student Support
This area refers to student experiences outside the classroom, including support services and on and off-campus co-curricular activities.
SUPPORT 3, Standard 1: Co-curricular opportunities
S3.S1 Students have equitable and affordable access to co-curricular opportunities for networking, leadership, and experiential learning including global cultures and breadth of perspectives.
SUPPORT 3, Standard 2: Career Support
S3.S2 Students develop relationships with employers through career advising to navigate the sustainability careers watershed including developing a sustainability resume, and gaining real-world experience through internship/externship/fellowship
SUPPORT 3 Standard 3: Extracurricular Offerings
S3.S3 Students have equitable and affordable access to extracurricular opportunities for networking, leadership, and experiential learning including non-Western perspectives and global cultures.
SUPPORT 3, Standard 4: Equitable Financial Support
S3.S4 Financial support is provided to intentionally support students of diverse backgrounds underrepresented in environmental and sustainability careers
Support Area 4: Faculty Support
This area describes policies and practices for faculty teaching sustainability courses or leading sustainability initiatives.
SUPPORT 4, Standard 1: Professional Development
S4.S1 Faculty across disciplines have access to Professional Development for Sustainability, Climate Change, Resilience, and Environmental Literacy and Education in order to create coherence and maintain currency and relevance across academic disciplines.
SUPPORT 4, Standard 2: Incentivizing Interdisciplinary Engagement
S4.S2 Minimum Qualifications and criteria for tenure and promotion reflect and support interdisciplinary engagement in sustainability education.
SUPPORT 4, Standard 3: Sustainable Workload
S4.S3 Faculty appointments, workload formulas, scheduling, and class sizes (large or small) are optimized and appropriately consider faculty wellbeing as well as sustainability teaching & learning practices which are interdisciplinary, experiential, and collaborative.
SUPPORT 4, Standard 4: Sustainability and Open Knowledge
S4.S5 Faculty scholarship and research includes and values Sustainability, Collaboration, and Open Knowledge Practices. (If your institution or program does not include research or publication requirements, skip this one.)